QUALITY TOOL: BRAINSTORMING

Basics
Based on Quality Capsule 10, we are probably now adept at Analysing a Flow Diagram.
In this Quality Capsule, I wish to share some interesting techniques for Brainstorming.
Let us start with, why should we use brainstorming? My answer: To get team members to pool their knowledge and creativity, in generating “waves” of ideas, while diagnosing a chronic problem, as well as designing a remedial solution.
Please reread the sentence and revisit Quality Capsule 5 on Structured Quality Improvement.
Next, what does brainstorming do? My answers:
- Discourage “same old way” of thinking, by creating more and more ideas that team members can build upon
- Allow each person to be creative while focusing on a team’s common objective.
Finally, what does it mean to be creative? My answers:
- To consistently produce a volume of ideas
- To put existing or new ideas together in multiple combinations
- To make connections between the chronic problem and seemingly unrelated facts or observations.
Four Phases of Brainstorming
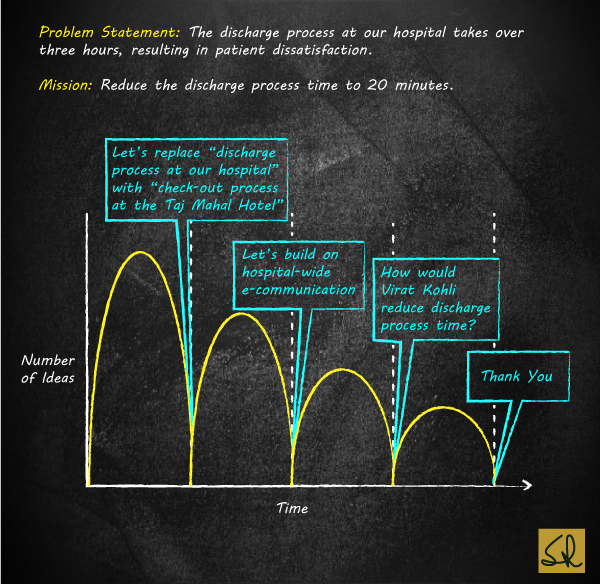
Potential Misapplications and Pitfalls
Brainstorming is not a substitute for data. This is the most serious misapplication.
While brainstorming is a very useful tool for Structured Quality Improvement, it cannot be used to:
- Prioritize projects
- Analyze the symptoms
- Test hypotheses
- Identify the root cause
- Verify the effectiveness of a solution.
Recommendation
In order to stimulate right-brain creative thinking, I recommend that team members be trained on:
- Classic Brainstorming
- Imaginary Brainstorming
- Brainwriting 6-3-5
Insight
For a brainstorming session, a related flow diagram can facilitate a flood of ideas.
An effective surgeon works with multi-tools. An effective qualitist also works with multi-tools. Do you agree?
Next
In my next edu-blog, on Wednesday 23 September, I will introduce Cause-Effect Diagrams.
